Anxiety
Anxiety
When someone is exposed to any form of stress, the body will always respond to the situation. Anxiety is a natural response of the body to stress, and it occurs as a feeling of apprehension or fear of what is about to come.
Usually, a bit of nerves is a healthy and normal emotion that many people experience. However, in some cases, people experience disproportionate degrees of anxiety, indicating a medical condition. As a mental disorder, anxiety results in high levels of worry, apprehension, fear, and nervousness. Anxiety disorders affect how an individual behaves and processes emotions. When anxiety is severe, it will affect the day-to-day living of a person. Our Orange County anxiety treatment center is here to help with severe cases.

Anxiety By the Numbers
Anxiety disorders are among the most highly prevalent mental disorders in the United States. They affect about 40 million individuals who are above 18 years old in the nation. In particular, this represents about 18.1% of the American population, which is affected by the condition each year.(1)
Though all anxiety diseases can be effectively treated, only about 36.9% of people with anxiety get treated for this disorder. Importantly, about 31.1% of people in the U.S. develop an anxiety disorder at some point in their life.(2)
The number of women who develop anxiety disorders are higher compared to men. Additionally, when a person has an anxiety disorder, they are more likely to visit a doctor and are six times more probable to be hospitalized for disorders of psychiatric nature compared to those who don’t have an anxiety disorder.
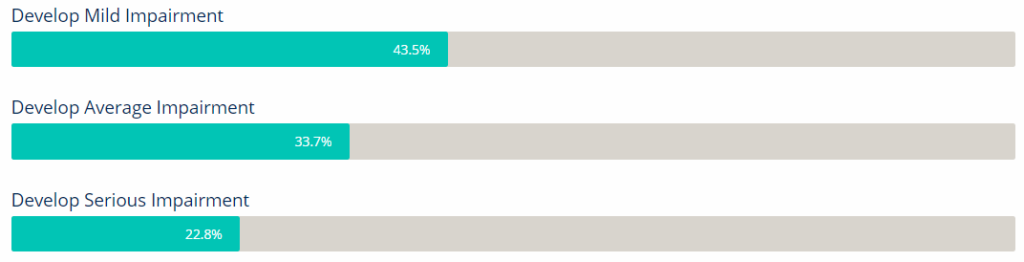
Adolescent Anxiety

Types of Anxiety Disorders
Causes of Anxiety
Symptoms of Anxiety
The symptoms of anxiety would vary from one individual to another. While some experience feelings that causes butterflies in the stomach, other people could have feelings that lead to a rapid heart rate. Usually, there would be disconnect between the body and the mind, and this would make an individual feel out of control. In other situations, individuals with anxiety could have painful thoughts, panic attacks, and nightmares.
A common feeling of worry and fear is typical in most of the anxiety disorders. Importantly, the symptoms would change depending on the type of anxiety that an individual is experiencing. Mainly, the following are the critical general symptoms that people with anxiety would show. Our Orange County anxiety treatment center is dedicated to addressing all of these symptoms.
RESTLESSNESS AND A FEELING OF BEING "ON-EDGE"
In people with any type of anxiety disorder, restlessness is a typical symptom. It is even more common in teens and children than in adults. Usually, this comes as an unpleasant desire to move.
In a particular survey that had 128 kids who had anxiety as the participants, the researchers established that 74% of the respondents indicated restlessness as being among the main symptoms of anxiety.5
In most of the cases, physicians use restlessness as an indication that a person has an anxiety disorder. If someone experiences this symptom in most of the days, and for about six months or more, then this could indicate anxiety disorder in the individual.
UNCONTROLLABLE FEELINGS OF WORRY
Excessive worrying is another symptom of anxiety that is most common and regular. In essence, this type of worrying is uncontrollable, and the people with this disorder would have little to do in alleviating the level of worry.
Additionally, this worry would be disproportionate in relation to the situations that trigger it.5 Mostly, the worry would occur in reaction to situations that are normal in the day-to-day life. The worry is usually severe and would make it hard for a person to accomplish daily chores. The feeling of worry could last for up to six months or more.
INCREASED IRRITABILITY
TENSE MUSCLES
SLEEP DIFFICULTIES
CONCENTRATION DIFFICULTIES
Orange County Anxiety Treatment
Some medications could be used to deal with anxiety in individuals. Sedatives and antidepressants are a few examples. They deal with the symptoms, control anxiety episodes, and establish a balance of brain chemistry.
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepine is an example of a sedative that is commonly used in healthcare settings. They act by depressing the nervous system which would be essential in addressing an anxiety disorder.
SSRIs
Mainly, these drugs are used as antidepressants in the management of mental situations. They also help in the treatment of anxiety disorders and other depressive disorders.
Prevention of Anxiety

Finding Help With Anxiety and Addiction

We Work With Most Major
Insurance Providers
The Safe Harbor Treatment Center Admissions Team works to ensure that we can help as many people struggling with substance abuse. Verify your benefits now and we’ll get back to you right away.
Receive the highest level of care available at Safe Harbor. We are here to answer your call or fill out our confidential contact form to get started.
ADAA. (2017). Facts & Statistics. Retrieved on 12 June 2019, from https://adaa.org/about-adaa/press-room/facts-statistics
APA. (2017). What Are Anxiety Disorders? Retrieved on 12 June 2019, from https://web.archive.org/web/20220727182912/https://psychiatry.org/Patients-Families/Anxiety-Disorders/What-are-Anxiety-Disorders
Bandelow, B., & Michaelis, S. (2015). Epidemiology of anxiety disorders in the 21st century. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 17(3), 327.
CDC. (2019). Data and Statistics on Children’s Mental Health. Retrieved on 12 June 2019, from https://www.cdc.gov/childrensmentalhealth/data.html
Julson, E. (2018). 11 Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders. Retrieved on 12 June 2019, from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/anxiety-disorder-symptoms#section7
NIH. (2017). Any Anxiety Disorder. Retrieved on 12 June 2019, from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/any-anxiety-disorder.shtml
Schoneveld, E. A., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A., & Granic, I. (2018). Preventing childhood anxiety disorders: is an applied game as effective as a cognitive behavioral therapy-based program?. Prevention Science, 19(2), 220-232.
Snyder, M., & Zubernis, L. (2016). Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Effective Case Conceptualization Using the Temporal/Contextual Model. American Counseling Association.

